Robotic Process Automation “RPA” is a software programme, which using recorders and easy programming language imitates human execution of applications, usually for repetitive tasks. Business users control user-friendly configurations and govern it. RPA repeats human interactions with proven technology. It performs common tasks such as queries, cut/paste, merging, button clicks, etc.
One of the popular definition of “Robotic Process Automation” is –
“An application of technology that allows employees in a company to configure computer software, or a ‘robot’, to capture and interpret existing applications for processing a transaction, manipulating data, triggering responses and communicating with other digital systems”.
-The Institute for Robotic Process Automation (IRPA)
Robotic Process Automation is not a physical robot sitting at a desk performing tasks. It is a new alternative to improve productivity, unlocking higher Return on Investment than ERP implementations and Software as a Service (SaaS) which requires more investment in terms of time and cost.
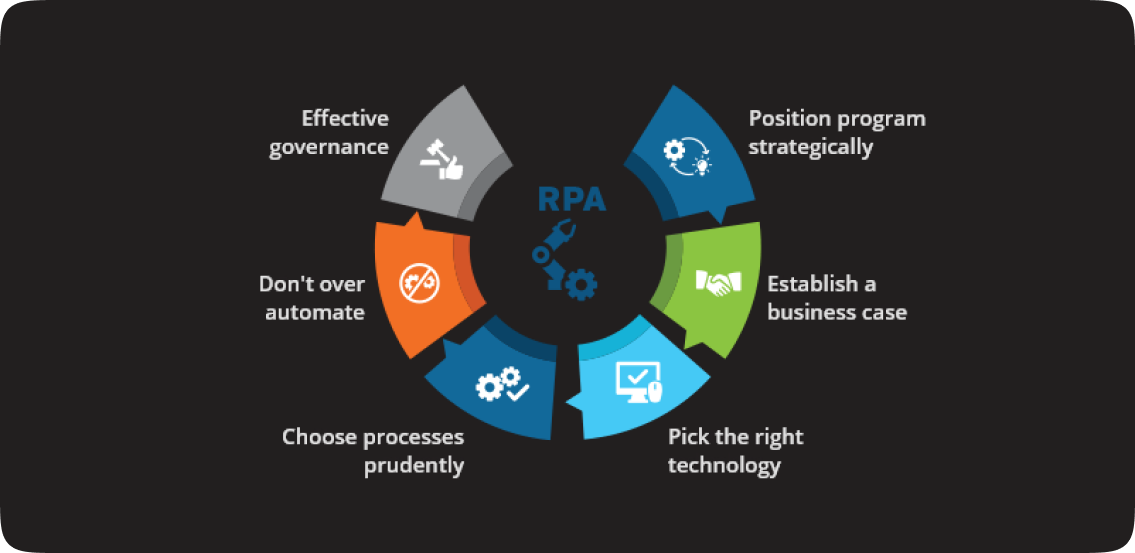
It is the first step and necessary foundation in the enterprise digital operation journey, before implementing cognitive, chatbots and artificial intelligence.
Key objectives of implementing Robotic Process Automation are as follows –
- Improve customer experience
- Improve accuracy
- Manage controls
- Higher efficiency
- Reduction of monotonous work
- Cost saving
- Skill upgradation of personnel
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the next phase of innovation in the world. It’s significant potential to become a differentiator has become evident. Most of the notable players are either assessing possibilities to benefit from this new solution or even proceeding with the first implementations.
Once IT and security risks are satisfied with the IT architecture, the process is documented in detail and can be carried forward for implementation.
Key sectors where RPA is playing a significant role in bringing in process efficiencies include highly regulated verticals such as,healthcare,banking, financial services and insurance. Other major sectors include telecommunications, utilities, mining, travel and retail.
Functional Areas where RPA implementation is beneficial are as under:
- Human Resources
- Payroll Administration
- Benefits Enrolment
- Data of Employees Management
- Management of Claims
- Tracking of Leave Applications
- Routine Query Management
- Finance & Accounting
- Accounts Receivable (OTC)
- Procurement/ Sourcing
- Order Management
- Invoice Processing
- Billing Management
- Records to Report (RTR)
- Customer Services
- Billing Support
- Query Management
- Compliance Management
- Order Processing
- Sales Management
- Subscription Management








